BACnet
BACnet (Building Automation and Control Networks) is an automation protocol that has been developed for building automation and is constantly being further developed. First and foremost, it ensures the interoperability of devices from different manufacturers with each other. BACnet/IP uses the Internet protocol as the communication layer, and BACnet/SC provides authenticated and encrypted communication between BACnet devices.
This chapter describes how to configure the BACnet service on the Beetle and start a network query via BACnet.
Please ensure that your Beetle is in operation and has a connection to the Avelon server. If this is not the case, start in the chapter Connectivity.
Warning
There are some reserved IP addresses that the Beetle uses to communicate. Please avoid using any of these addresses in your network.
Note
To use the BACnet service on the Beetle, you need a valid BACnet licence.
Note that two separate licenses are required to use BACnet/IP and BACnet/SC, respectively.
Enable BACnet service
In order to use the BACnet service and read network objects, a valid licence key must be stored and the service must be enabled. How to enable or license communication protocol services is described in section Communication protocols.
Configure service
Note
To configure the BACnet service, you must have operator privileges.
Click on BACnet on the left.
Click the Settings button to open the configuration dialog of the BACnet service and edit parameters.
General BACnet settings
These settings are available for any communication mode (IP or SC).
- Communication mode
Select which mode the Beetle should use to communication with BACnet devices:
IP
SC
IP and SC
- Device ID
The device identification number of the Beetle. Allowed values are 0 - 4194304, the default value is 100.
- Time synchronization
The Beetle automatically adjusts the time on the connected BACnet devices to its own time. Select the desired time synchronization mode.
Off
Local time
UTC
- Interval
Select how frequently the time should be synchronized.
Hourly
Daily
Weekly
- Refresh DNS
Select how often the DNS on the Beetle should be refreshed.
Never
Hourly
4 × Daily
Daily
BACnet/IP-specific settings
These settings are only available if Communication mode is set to “IP” or “IP and SC”.
- Network ID
The BACnet/IP network identification number of the Beetle. Allowed values are 0 - 65535, the default value is 1.
If you want to use BACnet/IP and BACnet/SC simultaneously, the network ID for BACnet/IP and BACnet/SC have to be different.
- UDP port
Set the port on which BACnet/IP should listen. Allowed values are 47808 - 47817, the default value is 47808.
- Network interface
If two network cards are configured, select the interface via which the controllers are accessed here. Otherwise leave the value at LAN.
LAN
WAN
- Enable BACnet routing
Enable this option if you want the Beetle to act as a BACnet router, interconnecting multiple BACnet/IP networks.
This option needs to be enabled if you want to use a BACnet client via Avelon Connect, or if you want to route two different BACnet networks through the Beetle. Otherwise, the option should be disabled to avoid unnecessary routing.
- Use port hierarchy
By default, there is one base level Network Port object with IP mode “normal” and protocol level “BACnet application” configured, as well as multiple Network Port objects (one for each foreign device/BBMD) with IP mode “foreign” and the reference port set to the base port.
If you require a setup where only a single Network Port object is present, you can disable the port hierarchy with this option. In that case, only one Network Port object with IP mode “foreign” will be created.
BACnet/SC-specific settings
These settings are only available if Communication mode is set to “SC” or “IP and SC”.
- Network ID
The BACnet/SC network identification number of the Beetle. Allowed values are 0 - 65535, the default value is 1.
If you want to use BACnet/IP and BACnet/SC simultaneously, the network ID for BACnet/IP and BACnet/SC have to be different.
- TCP port
Set the port on which BACnet/SC should listen. Allowed values are 47808 - 47817.
- Node type
Select which type of node the Beetle should represent in the BACnet/SC network:
Regular node
Primary hub
Failover hub
- Primary hub URI
Enter the URI of the primary hub. The field is mandatory if Node type is set to Regular node.
- Failover hub URI
Enter the URI of the failover hub. The field is mandatory if Node type is set to Regular node.
Certificates
In order to create a certificate for the Beetle, follow these steps:
Click on Create CSR.
Enter all required fields in the dialog.
- Common name
This is the fully qualified domain name that you wish to secure.
- Organization name
Usually the legal name of a company or entity and should include any suffixes such as Ltd., Inc., or Corp.
- Organizational unit
Internal organization department/division name.
- Locality
Name of the town, city, village, etc.
- State
Province, region, county or state. This should not be abbreviated (e.g. West Sussex, Normandy, New Jersey).
- Country
The two-letter ISO code for the country where your organization is located.
- Email address
The organization contact, usually of the certificate administrator or IT department.
Click on OK. This will generate and download the CSR.
Go to the designated Avelon server (Avelon Cloud, Alcedo Inhouse or WAGO Building Cloud Services). To do that, you can click on the link that is displayed on the Home page next to Avelon server.
On the Avelon server, log in and click on your name in the top right corner, then on Devices.
Select any Beetle in the device list and navigate to the Objects on the Network tab.
In the sidebar on the left, make sure BACnet is selected in the dropdown at the top.
Next to the dropdown, click on More ▸ Manage BACnet/SC Networks….
On the BACnet/SC Networks view, select the correct BACnet/SC network in the sidebar on the left.
If the device is already in the list, click on Renew Certificate next to the respective device. Otherwise click on Add Device at the top right to add a new device.
In the dialog Create New Certificate, enter the BACnet ID of the Beetle for which you just created the CSR and upload the CSR file in the field Certificate Signing Request. Click on Generate.
A new certificate will be generated for the device, and a new item appears in the list. At the same time, you will be prompted to download the certificate files. You can re-download the certificate and CA certificate at any time by clicking on the Download Certificates link on the BACnet/SC Networks view. Download them to your computer, then go back to the Beetle user interface and upload the two files in the fields Certificate and CA certificate, respectively. Save the configuration.
BBMD
If BACnet/IP is enabled, you can set the mode in which the Beetle should operate. Click on BBMD to open the BBMD (BACnet broadcast management device) configuration.
Select the desired mode in the dropdown. Depending on the selection, you can add one or more devices to the list below.
- Simple device
The Beetle acts as a simple BACnet device.
- Foreign device
The Beetle acts as a foreign device. A foreign device is a BACnet device that has an IP subnet address that is different from the IP subnet address that includes the BACnet/IP network that the device wants to join. Although the device can communicate directly with other BACnet devices, it receives broadcasts from other devices only if it is registered with the corresponding BBMD. Add all BBMDs to the list below by clicking on Add and entering their respective IP address and BACnet/IP port.
- BBMD
The Beetle acts as a broadcast management device. Add all BACnet devices to the list below that the Beetle needs to communicate with by clicking on Add and entering their respective IP address, BACnet/IP port and subnet mask.
Warning
Foreign devices don’t send broadcast messages. Instead, they require a local BBMD to be able to discover other devices in the local network.
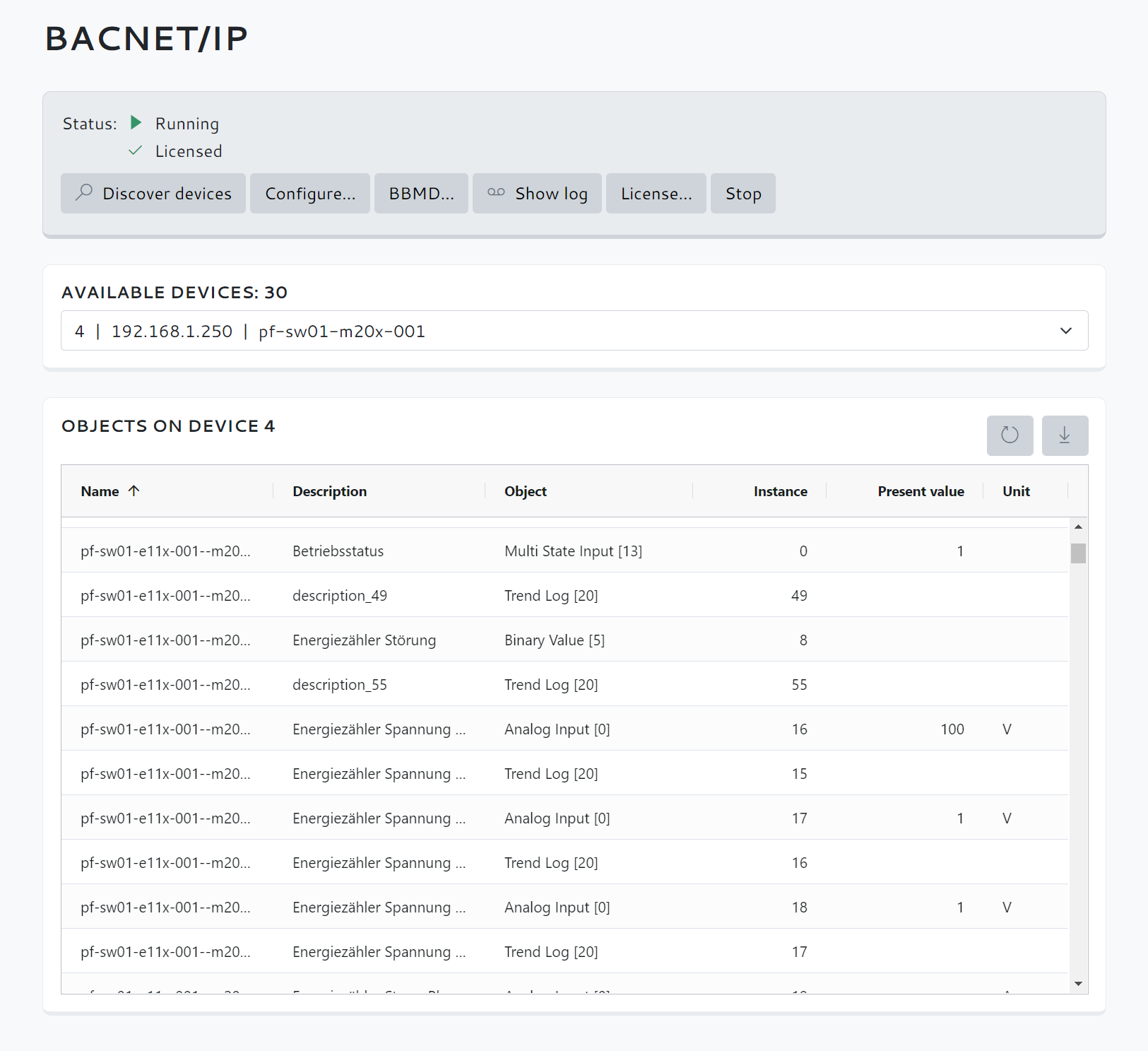
Scan network
On the BACnet page, click the Discover devices button to start a network discovery.
Note
If you receive the message “Please start the BACnet service to display objects on the network.”, you must first enable the BACnet service (see Enable BACnet service).
Warning
All network devices to be identified must be located in the same network segment.
After a short time, all network devices found are displayed.
Select one of the devices found to query its objects.
Note
Use this list to check that all objects are listed as expected. Only then should you adjust the data points via the Avelon user interface.
Download data point list (optional)
After a successful network scan, click the Download button to download the list of found objects to your computer as a CSV file.