Modbus TCP
This chapter describes how to configure the Modbus TCP service on the Beetle and how to read and change the network objects.
Please ensure that your Beetle is in operation and has a connection to the Avelon server. If this is not the case, start in the chapter Connectivity.
Warning
There are some reserved IP addresses that the Beetle uses to communicate. Please avoid using any of these addresses in your network.
Enable Modbus TCP service
In order to use the Modbus TCP service and read network objects, a valid licence key must be stored and the service must be enabled. How to enable or license communication protocol services is described in section Communication protocols.
Configure Modbus TCP service
Note
To configure the Modbus TCP service, you must have operator privileges.
Click on Modbus TCP on the left.
Click on the Settings button to open the communication settings of the Modbus TCP service and edit the parameters.
- Network interface
Select which network interface to which the Modbus TCP service should be bound. If you select Any, the Beetle will determine the appropriate interface automatically.
- Pause between reading live values
Pause in milliseconds that the Beetle should wait between reading live values.
- Response timeout
The timeout interval in milliseconds used to wait for a response. If no response is received after this timeout, the request will be aborted.
- Byte timeout
The timeout interval in milliseconds between two consecutive bytes of the same message. If no byte is received after this timeout, the request will be aborted.
- Keep connection open
If enabled, the same TCP connection will be used between successive requests (recommended). The connection will only be closed when no requests are pending, or when a timeout or any other kind of error occurs. If disabled, a separate TCP connection will be opened for each request.
- Enable range reading
If enabled, the service will read a range of objects per request. If disabled, each object will be read with a separate request.
Confirm the changes by clicking on OK.
To define which devices, slaves and objects you want to access through Modbus, click on the Configuration files button.
In the dialog, click the Upload Configuration File button to upload a new XML configuration file. You can always delete configuration files that have already been uploaded by clicking the Delete button or download them to your computer by clicking the Download button.
Note
The configuration files are used to define the objects that are offered via the Modbus TCP service. The object list is stored statically and not dynamically queried by the bus.
For a list of the supported data types, see Supported Modbus data types.
For a list of possible error codes, see Modbus error codes.
Create configuration file
The configuration file for Modbus must be created in a specific XML format. With the Avelon Modbus Configurator, an Excel-based workbook, such configuration files can be created semi-automatically.
Open the Avelon Modbus Configurator in Excel.
Click on the Neues Blatt (New Sheet) button to create a new Modbus configuration.
First configure the connection data to the target device in the upper section.
Then define the individual bus objects in the area below. For each object use a new row and fill in all fields.
Finally, click Exportieren (Export) to generate the configuration file and save it on the computer to save it. You can decide whether only the current worksheet or all worksheets of the current folder are to be exported.
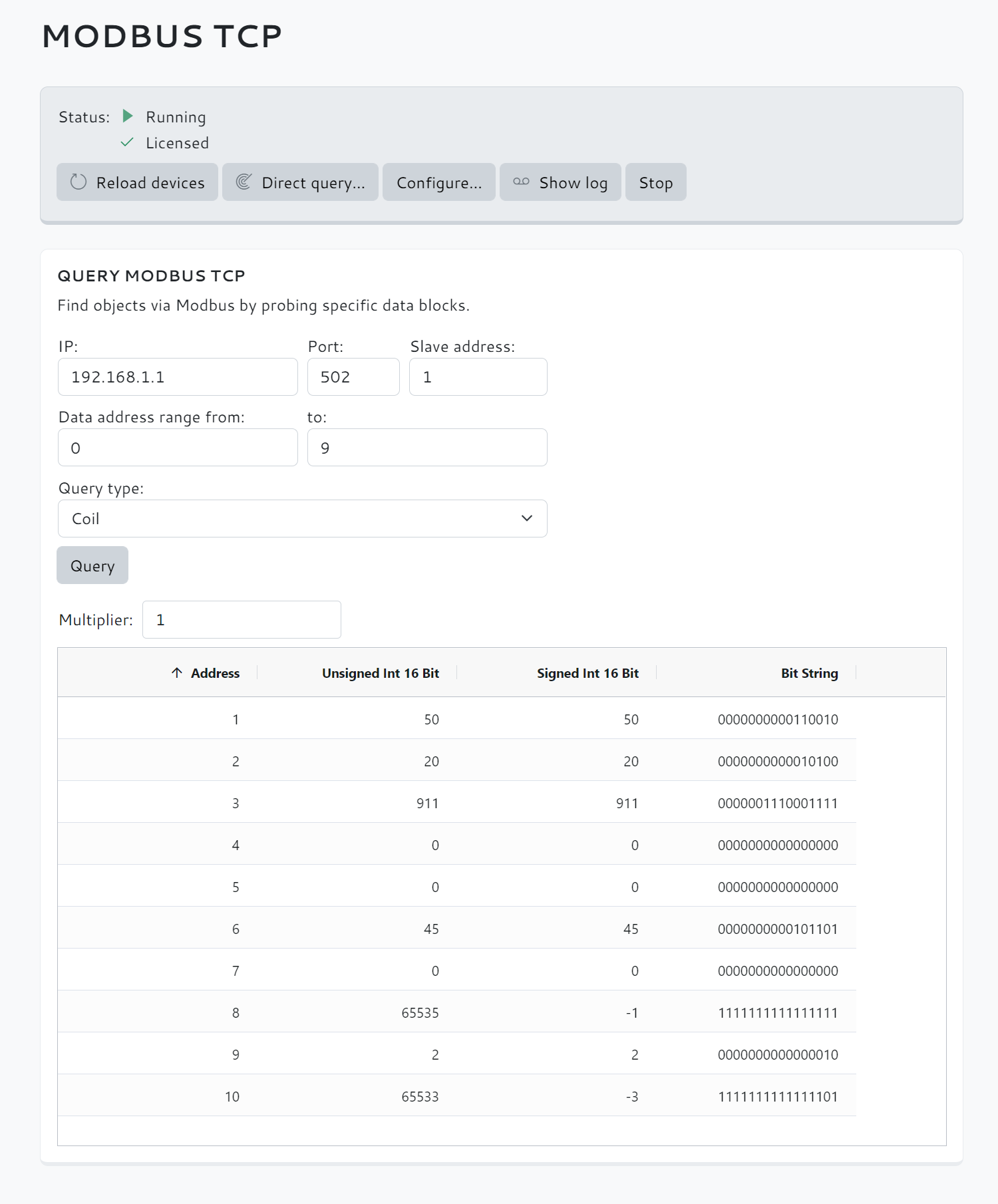
Query bus addresses directly
To check whether the objects can be read correctly via Modbus TCP, click the Direct query… button.
In the following dialog you can set which address range is to be read out and how the individual bytes are to be interpreted.
- IP and port
The IP address and port where the Modbus device can be reached. The standard port for Modbus is 502.
- Slave address
The device number of the Modbus device to be queried.
- Data address range
Start and end address of the range to be queried.
- Data type
Select the data type that should be used to query the values. Coil or Discrete Input will query single bits, while Input Register or Holding Register will query entire registers.
- Size
Select the size of the registers in bits.
16 (= 2 Bytes)
32 (= 4 Bytes)
64 (= 8 Bytes)
- Byte order
Select in which order the individual bytes are stored in memory.
Big endian: The most significant byte is stored at the smallest memory address.
Little endian: The most significant byte is stored at the largest memory address.
- Word order
If you want to query registers with more than 16 bits, you can select the order of the individual words in memory.
Big endian: The most significant word is stored at the smallest memory address.
Little endian: The most significant word is stored at the largest memory address.
Then click the Query button to read the address range. The result is displayed in a table below the search mask. Further display options are now available below:
- Multiplier
The values read out are multiplied by this number. Use this function if the actual value is a multiple of the stored value.
Show objects
On the Modbus TCP page, click the Reload gateways button to reload the gateways and objects that you have previously configured using the uploaded configuration files.
Note
If you receive the message “Please start the Modbus TCP service to display objects on the network.”, you must first enable the Modbus TCP service (see Enable Modbus TCP service).
The gateways from the uploaded configuration files are displayed immediately. Select one of the gateways to display its devices. Then click one of the devices to list the objects defined on it.
Note
Use this list to check that all items are available as expected. Only then should you adjust the data points via the Avelon user interface.
Download data point list (optional)
After successful object retrieval, click the Download button to download the list of objects to your computer as a CSV file.